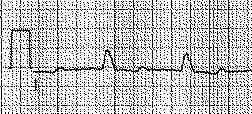

The systolic excursion of the mitral annulus can be displayed as a loop of serial echocardiographic frames. The motion can be used to assess function of the interventricular septum in patients with paradoxic septal motion due to left bundle branch block. This helps distinguish true hypokinesis from altered septal motion purely due to the conduction abnormality.
Sohn DW, Chai IH, Lee DJ, Kim HC, Kim HS, Oh BH, Lee MM, Park YB, Choi YS, Seo JD, Lee YW. Assessment of mitral annulus velocity by Doppler tissue imaging in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997 Aug;30(2):474-80
OBJECTIVES: This study assessed the clinical utility of mitral annulus velocity in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. BACKGROUND: Mitral inflow velocity recorded by Doppler echocardiography has been widely used to evaluate left ventricular diastolic function but is affected by other factors. The mitral annulus velocity profile during diastole may provide additional information about left ventricular diastolic function. METHODS: Mitral annulus velocity during diastole was measured by Doppler tissue imaging (DTI) 1) in 59 normal volunteers (group 1); 2) in 20 patients with a relaxation abnormality as assessed by Doppler mitral inflow variables (group 2) at baseline and after saline loading; 3) in 11 patients (group 3) with normal diastolic function before and after intravenous nitroglycerin infusion; and 4) in 38 consecutive patients (group 4) undergoing cardiac catheterization in whom mitral inflow velocity and tau as well as mitral annulus velocity were measured simultaneously. RESULTS: In group 1, mean +/- SD peak early and late diastolic mitral annulus velocity was 10.0 +/- 1.3 and 9.5 +/- 1.5 cm/s, respectively. In group 2, mitral inflow velocity profile changed toward the pseudonormalization pattern with saline loading (deceleration time 311 +/- 84 ms before to 216 +/- 40 ms after intervention, p < 0.001), whereas peak early diastolic mitral annulus velocity did not change significantly (5.3 +/- 1.2 cm/s to 5.7 +/- 1.4 cm/s, p = NS). In group 3, despite a significant change in mitral inflow velocity profile after nitroglycerin, peak early diastolic mitral annulus velocity did not change significantly (9.5 +/- 2.2 cm/s to 9.2 +/- 1.7 cm/s, p = NS). In group 4, peak early diastolic mitral annulus velocity (r = -0.56, p < 0.01) and the early/late ratio (r = -0.46, p < 0.01) correlated with tau. When the combination of normal mitral inflow variables with prolonged tau (> or = 50 ms) was classified as pseudonormalization, peak early diastolic mitral annulus velocity < 8.5 cm/s and the early/late ratio < 1 could identify the pseudonormalization with a sensitivity of 88% and specificity of 67%. CONCLUSIONS: Mitral annulus velocity determined by DTI is a relatively preload-independent variable in evaluating diastolic function.
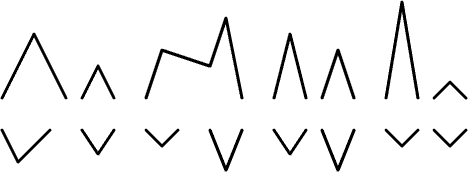 Mitral inflow Doppler with corresponding mitral annulus
tissue Doppler below, in the following four diastolic left
ventricular filling conditions: normal, abnormal relaxation,
pseudonormal and restrictive.
Mitral inflow Doppler with corresponding mitral annulus
tissue Doppler below, in the following four diastolic left
ventricular filling conditions: normal, abnormal relaxation,
pseudonormal and restrictive.
Back to E-chocardiography Home Page.
e-mail:shindler@umdnj.edu