

Atrial flutter can cause characteristic M-mode deflections of the mitral leaflets.
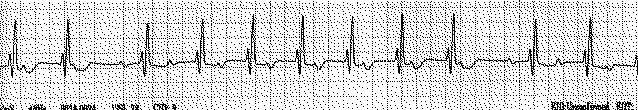
Electrocardiographic features: progessive PR interval prolongation with eventual complete AV block manifested as a P wave that is not followed by a QRS complex.
Echocardiographic implications: the resultant cyclic variability in the mitral inflow pulsed wave Doppler pattern may be misinterpreted as respiratory variation if the electrocardiographic pattern is unrecognized.
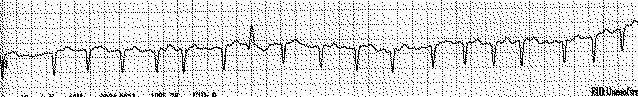
Electrocardiographic features: QRS widening and altered morphology when a short RR interval follows a long RR interval. The rhythm in this tracing is atrial fibrillation, hence the variability in the RR interval.
Echocardiographic implications: mitral and tricuspid leaflet motion
and pulsed wave Doppler ventricular inflow patterns may remain unaltered
compared to the cardiac cycles with a normal QRS. The echocardiographic
flow pattern may be helpful in the electrocardiographic differentiation
between aberrant supraventricular and premature ventricular beats.
As opposed to a premature ventricular beat, this wide QRS complex is of
supraventricular origin. It is less likely to disrupt the sequence of
atrio-ventricular filling.
Back to E-chocardiography Home Page.
e-mail:shindler@umdnj.edu The contents and links on this page were last verified on September 26, 2002.