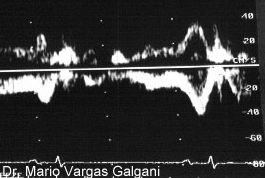
Pulsed wave Doppler from the pulmonary artery. There is diastolic antegrade flow in the pulmonary artery that increases with atrial contraction.

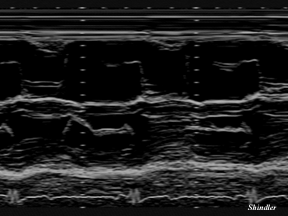
M-mode in Ebstein anomaly of the tricuspid valve can simultaneously display both the tricuspid and the mitral valve opening.
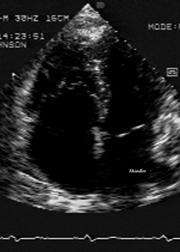
2D shows exaggerated apical displacement of the tricuspid valve.
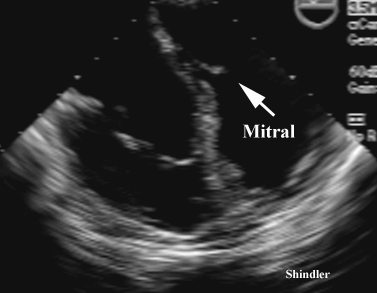
Transesophageal appearance of Ebstein anomaly.

The chest x-ray shows cardiomegaly with right side enlargement, clear lungs, and a small hilum.
Case report and review of the perinatal implications of maternal lithium use.
Pinelli JM, Symington AJ, Cunningham KA, Paes BA.
School of Nursing and the Department of Pediatrics, McMaster University, Faculty of Health Sciences, Hamilton, Ontario Canada.
The purpose of this study was to review the use of lithium in pregnancy and its effects on the neonate. This was a case study and review of the published literature.Lithium is commonly used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders, specifically bipolar depression. Bipolar disorders that require treatment with lithium demand special consideration when the woman becomes pregnant. Reported neonatal problems with maternal lithium therapy include Ebstein's anomaly, poor respiratory effort and cyanosis, rhythm disturbances, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, thyroid dysfunction, hypoglycemia, hypotonia and lethargy, hyperbilirubinemia, and large-for-gestational-age infants.Lithium can have adverse effects on the fetus and newborn infant, but data suggest normal behavioral patterns in childhood.
Lancet 1992 Feb 29;339(8792):530-3
Prospective multicentre study of pregnancy outcome after lithium exposure during first trimester.
Jacobson SJ, Jones K, Johnson K, Ceolin L, Kaur P, Sahn D, Donnenfeld AE, Rieder M, Santelli R, Smythe J, et al.
Department of Pediatrics and Pharmacology, Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Lithium carbonate is an effective drug for prophylaxis and treatment of major affective disorders. In-utero exposure to lithium during the first trimester of pregnancy might be associated with an increased risk of cardiac malformations, especially the rare Ebstein's anomaly. We prospectively recruited and followed 148 women (mean age 30 years, SD 5 range 15-40) using lithium during the first trimester of pregnancy, who consulted four teratogen information centres in the USA and Canada. Pregnancy outcome was compared with that of controls matched for maternal age. We had complete follow-up of pregnancy outcome in 138 of 148 patients recruited. In the other 10, fetal echocardiograms were available but postnatal follow-up was not done. Mean daily dose of lithium was 927 mg (SD 340). Rates of major congenital malformations did not differ between the lithium (2.8%) and control (2.4%) groups. 1 patient in the lithium group chose to terminate pregnancy after Ebstein's anomaly was detected by a prenatal echocardiogram. There was 1 ventricular septal defect in the controls. Birthweight was significantly higher in the lithium-exposed infants than in the controls despite identical gestational ages (3475 [660] g vs 3383 [566] g, p = 0.02). The true difference in birthweight might have been even larger, since significantly more women using lithium than controls were cigarette smokers (31.8% vs 15.5%, p = 0.002). These results indicate that lithium is not an important human teratogen. Women with major affective disorders who wish to have children may continue lithium therapy, provided that adequate screening tests, including level II ultrasound and fetal echocardiography, are done.
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome and Ebstein Anomaly of the Tricuspid Valve
An Esp Pediatr. 1990 Jun;32(6):522-30.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: long-term follow up study in a pediatric population
(86 cases)
Gonzalez de Dios J, Rodriguez Balo A, Martinez de Azagra Garde A, Benito Bartolome F,
Cabo Salvador J, Moreno Granado F.
Servicio de Cardiologia, Clinica Infantil La Paz, Madrid.
Eighty six patients (48 males and 38 females) with W-P-W diagnosed before the age of 15 years had a maximum follow-up of 20 years. The mean age at diagnosis was 3 y and 5 m., most cases being concentrated in the first 6 months of life (37%). Twenty seven (31.4%) had associated heart disease, the more common being: ventricular septal defect (6 cases), Ebstein malformation (5 cases) and transposition of the great arteries (4 cases). Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) was the commonest form of clinical presentation, followed by examination because heart murmur or heart disease. Fifty patients (58%) had SVT along the follow-up. SVT was more frequent in W-P-W type A than in type B (p less than 0.05). There was a statistically significant correlation (p less than 0.001) between the association of SVT and the absence of heart disease, but the finding must be questioned because the true incidence of W-P-W in normal population is unknown. There also were a significant correlation (p less than 0.05) between the association of W-P-W type B and the presence of heart disease. An electrophysiologic study was performed in 11 patients, 6 of them being concealed W-P-W. Four patients were operated upon because of SVT. We have studied a total of 154 SVT episodes in the 50 patients with SVT. The treatment more frequently used to finish the SVT included: verapamil, DC-Countershock and Digoxin.
Back to E-chocardiography Home Page.

The contents and links on this page were last verified on March 28, 2006.