Pressure Flow and Derived Variables
Blood Gas Measurement Variables
Pulmonary Artery Occlusion Pressure
Definitions:
Afterload:
Ventricular wall stress during systole, as indicated by the Law of Laplace:
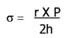
r = ventricular systolic dimensions
P = pressure during systole
h = wall thickness
Preload:
Ventricular wall tension (force / length) at the end of diastole
Contractility:
Measured by the slope of the end systolic pressure - volume relationship (end systolic elastance)
Arterial Impedance:
All factors that oppose ventricular ejection by absorbing the mechanical energy developed by the left ventricle (aortic impedence) or by the right ventricle (pulmonary artery impedence) during systole
Ventricular Compliance:
Ratio between a given stretch and the resulting tension in the relaxed isolated muscle
Ventricular Interdependence:
Diastolic volume and / or diastolic geometry influences diastolic pressure volume relationship of the contralateral ventricle
Pressure Flow and Derived Variables:
Measured Variables:
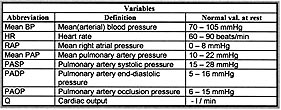
Calculated Variables:
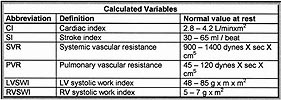
Systemic arterial blood pressure

Pulmonary artery pressure

Cardiac Index:
Cardiac Output divided by the Body Surface Area (BSA)
Body Surface Area

Stroke Volume and Stroke Index
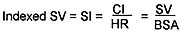
Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR)

SVR in GCS Measurements
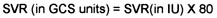
Pulmonary Vascular Resistance

Left Ventricular Stroke Work Index
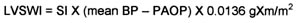
Right Ventricular Stroke Work Index

Blood Gas Measurement Variables:
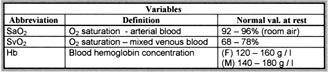
Measured Variables:
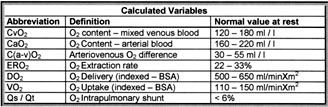
Calculated Variables:
Blood Oxygen Saturation
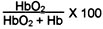
Blood Oxygen Saturation (Methemoglobinemia / CO Poisoning)
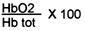
Oxygen Saturation of Mixed Venous Blood
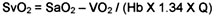
Oxygen Content of Blood
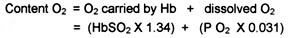
Oxygen Content - End Capillary Blood

Oxygen Delivery

Arteriovenous Oxygen Difference
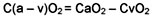
Oxygen Extraction
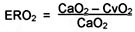
Oxygen Uptake (Principle)

Oxygen Uptake (Fick Method)
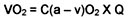
Pulmonary Artery Occlusion Pressure (PAOP):
PAOP and Pulmonary Capillary Filtration Pressure

- Aortic pressure diameter relation: changes in passive smokers. Full text article from the Annals of Internal Medicine.
- Cardiovascular simulations.
Back to E-chocardiography Home Page.
e-mail:shindler@umdnj.edu
The contents and links on this page were last verified on February 16, 2001.