Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis
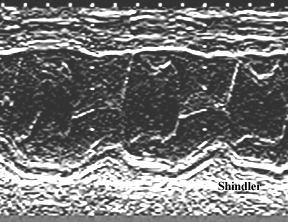
Systolic anterior motion of the mitral leaflets.
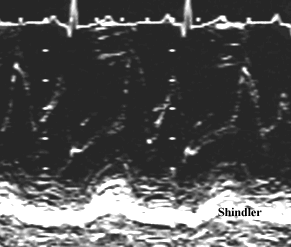
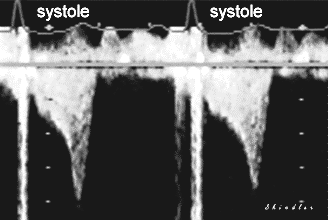
Late systolic obstruction on continuous wave Doppler examination of the left
ventricular outflow.
Brockenbrough Sign
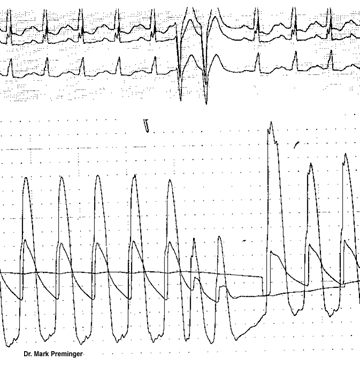
In hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy there is
a typical postextrasystolic pressure change in the left
ventricle and in the aorta. On the beat immediately
following a premature ventricular contraction:
- The left ventricular systolic pressure increases.
- The systolic gradient between the left ventricle
and the aorta increases.
- The aortic systolic pressure decreases.
- The aortic pulse pressure decreases.
Palpating the carotid pulse may provide evidence of the systolic
pressure drop. The amplitude of the very next beat following a premature
ventricular contraction may be decreased. Normally it would
be increased.
An echocardiographic technique to measure the left
ventricular ejection time (LVET) in the postextrasystolic
beat was shown to be more sensitive. LVET increased by
more than 20 msec in eleven of twelve patients with IHSS.
(Circulation 1975;52:306-312)
Synonyms for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
-
Asymmetrical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Asymmetrical hypertrophy of the heart
-
Asymmetrical septal hypertrophy
-
Brock's disease
-
Diffuse muscular subaortic stenosis
-
Diffuse subvalvular aortic stenosis
-
Dynamic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
-
Dynamic muscular subaortic stenosis
-
Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Familial hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
-
Familial muscular subaortic stenosis
-
Familial myocardial disease
-
Functional aortic stenosis
-
Functional hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
-
Functional obstructive cardiomyopathy
-
Functional obstruction of the left ventricle
-
Functional obstructive subvalvular aortic stenosis
-
Functional subaortic stenosis
-
Hereditary cardiovascular dysplasia
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Hypertrophic constrictive cardiomyopathy
-
Hypertrophic hyperkinetic cardiomyopathy
-
Hypertrophic infundibular aortic stenosis
-
Hypertrophic nonobstructive cardiomyopathy
-
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
-
Hypertrophic stenosing cardiomyopathy
-
Hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
-
Idiopathic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Idiopathic hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
-
Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
-
Idiopathic hypertrophic subvalvular stenosis
-
Idiopathic muscular hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
-
Idiopathic muscular stenosis of the left ventricle
-
Idiopathic myocardial hypertrophy
-
Idiopathic stenosis of the flushing chamber of the left
ventricle
-
Idiopathic ventricular septal hypertrophy
-
Irregular hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Left ventricle muscular stenosis
-
Low subvalvular aortic stenosis
-
Muscular aortic stenosis
-
Muscular hypertrophic stenosis of the left ventricle
-
Muscular stenosis of the left ventricle
-
Muscular subaortic stenosis
-
Muscular subvalvular aortic stenosis
-
Non-dilated cardiomyopathy
-
Nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Obstructive cardiomyopathy
-
Obstructive hypertrophic aortic stenosis
-
Obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Obstructive hypertrophic myocardiopathy
-
Obstructive myocardiopathy
-
Pseudoaortic stenosis
-
Stenosing hypertrophy of the left ventricle
-
Stenosis of the ejection chamber of the left ventricle
-
Subaortic hypertrophic stenosis
-
Subaortic idiopathic stenosis
-
Subaortic muscular stenosis
-
Subvalvular aortic stenosis of the muscular type
-
Teare's disease
Back to E-chocardiography Home Page.
e-mail:shindler@umdnj.edu
The contents and links on this page were last verified on
July 14, 2003.




