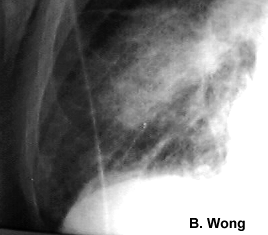

Echocardiography cannot image the lung findings of heart failure:
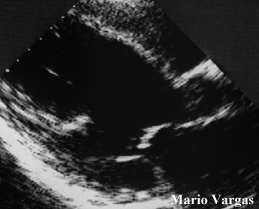 Dilated left ventricle with mitral chordal calcification.
Dilated left ventricle with mitral chordal calcification.
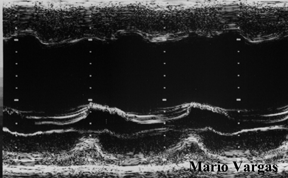 M-mode in the same patient showing increased E point
to septal separation.
M-mode in the same patient showing increased E point
to septal separation.
In patients with congestive heart failure, nonsustained ventricular tachycardia is an independent marker for increased overall mortality rate and sudden death. The absence of nonsustained ventricular tachycardia and ventricular repetitive beats in a 24-hour Holter indicates a low probability of sudden death.
BACKGROUND: The goal of the study was to determine the prognostic value of nonsustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT) in total mortality in severe congestive heart failure (CHF) and in death modes. NSVT is associated with an increased mortality in CHF. However, the predictive value of NSVT as a marker for sudden death or death due to progressive heart failure has not been determined. METHODS AND RESULTS: Five hundred sixteen patients from the GESICA trial (33.4% with NSVT) were initially studied with the results of 24-hour Holter and 2 years of follow-up. Within 2 years, 87 of 173 patients (50.3%) with NSVT and 106 of 343 patients (30.9%) without NSVT died. Relative risk (RR) was 1.69 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.27 to 2.24; P < .0002), and Cox proportional hazard analysis was 1.62 (95% CI, 1.22 to 2.16; P < .001). Sudden death increased from 8.7% (30 of 343) to 23.7% (41 of 173) in patients with NSVT (RR, 2.77; 95% CI, 1.78 to 4.44; P < .001). Progressive heart failure death was also increased from 17.5% (60 of 343) to 20.8% (36 of 173) (P = .22). Quantitative analysis of 24-hour Holter (first 295 patients) demonstrated that couplets had a similar RR to that of NSVT for both total mortality (RR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.22 to 2.66; P < .002) and sudden death (RR, 3.37; 95% CI, 1.57 to 7.25; P < .0005). Couplets and/or NSVT (ventricular repetitive beats) were even more predictive for sudden death (RR, 10.1; 95% CI, 1.91 to 52.7; P < .01). CONCLUSIONS: In patients with CHF, NSVT is an independent marker for increased overall mortality rate and sudden death. The absence of NSVT and ventricular repetitive beats in a 24-hour Holter indicates a low probability of sudden death.
Reference:
Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia in severe heart failure. Independent
marker of increased mortality due to sudden death. GESICA-GEMA
Investigators
Doval HC; Nul DR; Grancelli HO; Varini SD; Soifer S; Corrado G;
Dubner S; Scapin O; Perrone SV
Circulation 1996 Dec 15;94(12):3198-203
Comment in: Circulation 1997 Nov 18;96(10):3794-5
OBJECTIVE: This prospective clinical study investigated whether the relatively simple and cost-effective ultrasonography of the inferior vena cava (IVC) represents a valid clinical tool to assess the effectiveness of diuretic therapy in patients with chronic congestive heart failure (CHF). METHODS: Measurement of the resting and inspiratory diameter of the VCI repeatedly during diuretic therapy in 23 consecutive patients (11 women, 70 +/- 10 years) with CHF and comparing the results to the daily measured body weight and serum creatinine in these patients. Results were compared with the IVC diameter obtained in 33 healthy controls (16 women, 42 +/- 15 years). In addition, the IVC collapse index was calculated to assess inspiratory movements of the IVC in patients on day 1 and 10 of therapy. RESULTS: The IVC diameter at rest was 2.4 +/- 0.6 cm and decreased to 2.0 +/- 0.7 cm at inspiration, which was significantly greater than in healthy controls (1.4 +/- 0.4 cm at rest and 1.05 +/- 0.5 cm at inspiration; p = 0.008 and p = 0.01, respectively). The IVC diameter decreased continuously and significantly (p < 0.003) from day 1 to day 10 during diuretic therapy without a concomitant rise in serum creatinine. At beginning of therapy, the collapse-index of the IVC was significantly greater in patients than in controls. However, after 10 days of therapy this index reached similar values to those observed in controls. CONCLUSION: Ultrasonographic measurements of IVC diameter and inspiratory movements are a quantifiable and reliable approach to assess the hypervolemia associated with CHF. Normalization of inspiratory IVC collapse movement correlates with successful diuretic therapy and can be reliably used for bedside assessment and monitoring treatment in CHF patients.
Back to E-chocardiography Home Page.
e-mail:shindler@umdnj.edu
The contents and links on this page were last verified on October 17, 2002.